Mission Service
The Mission Service is a way for API clients to specify high level autonomous behaviors for Spot using behavior trees.
Behavior trees
Behavior trees allow clients to specify behaviors as simple as executing a sequence of tasks as well as more complicated behaviors, such as returning the robot to base when the battery is low. Behavior trees are commonly used in AI to define the behavior of non-player characters in video gaming.
Behavior trees consist of structural nodes that control how the tree is parsed, and action nodes, which carry out some action, such as making the robot navigate from place to place or activate a payload.
Each node may have zero or more children. Each child can be thought of as a distinct behavior tree, also called subtrees. For example, you can have a behavior tree that powers the robot on, then stands the robot up. That behavior tree can then be inserted as a child of another node.
Behavior tree blackboard
Certain action nodes depend on state that might be dynamically created by other nodes in the tree. State is written to and read from a blackboard, a messaging capability that allows nodes to share state in the behavior tree.
For example, the BosdynRobotState action node will read state from the robot, including whether or not motor power is on, and create a blackboard entry with the value of the state. The child of BosdynRobotState (and all of its children’s children) can read that information. Variables in the blackboard are scoped such that only the child of a node that defines a variable can read or write that variable.
If a node A defines a variable “MyVariable” and has a child node B, node B is allowed to also define “MyVariable” in the blackboard. Node B and its children will only be able to interact with Node B’s version of “MyVariable”.
Behavior tree node types
A behavior tree consists of a hierarchy of structural and action nodes.
Structural nodes control the order in which nodes are visited in mission execution or if they are visited at all.
Structural nodes
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Sequence | Specify a list of actions for the robot to perform. Child nodes are run in order until one of them fails. Sequences can be nested or combined with other structural node types. |
| Selector | Selectors run their child nodes in order until one of them succeeds. |
| Repeat | Loop a subtree a certain number of times. |
| Retry | Loop a subtree until it succeeds. |
| ForDuration | Loop a subtree until it fails. |
| SimpleParallel | Execute two nodes or subtrees at the same time. |
| Switch | Execute a specific child node based on a pivot value. |
Action nodes
Action nodes take some action, such as making the robot do something or triggering a payload to do something.
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| Condition | Express a binary comparison operation that returns true if the condition is true and false otherwise. |
| BosdynRobotState | Query robot service names, host, child nodes, battery, comms, E-Stop, kinematic and other robot system states. |
| BosdynRobotCommand | Issue a command to a robot to stop, freeze, self right, sit, stand, power off safely, go to a destination, or walk with some velocity. |
| BosdynPowerRequest | Power the robot on or off. |
| BosdynNavigateTo | Autonomously move the robot to a waypoint. Includes parameters for controlling properties, such as speed. |
| BosdynNavigateRoute | Autonomously move the robot along a route. Includes parameters for controlling properties, such as speed. |
| BosdynNavigateToAnchor | Autonomously move the robot to a pose in the GraphNav seed frame. Includes parameters for controlling properties, such as speed. |
| BosdynGraphNavState | Request the mission service to save graph nav state to the blackboard, where it can be accessed by a Condition node. |
| RemoteGrpc | Customize the behavior of missions. Example: trigger a remote sensor payload to take a reading during an autonomous mission. |
| Sleep | Sleep for a specified number of seconds. |
| Prompt | Prompt a supervisor with a question, such as "Is it safe to cross the street?" The supervisor can be a robot operator responding to a UI prompt or an automated process running anywhere that can communicate with the robot. |
| PTZ | Aim the Spot CAM PTZ at a specified pan, tilt, and zoom. Optionally, automatically adjust aim to offset differences in Spot positioning and orientation between playbacks. |
| SpotCamStoreMedia | Issue a request to write images to the Spot CAM USB stick. Note that an installed Spot CAM payload is required and the USB stick must be inserted before booting the robot. |
| Dock | Issue a command to dock the robot at the specified station. |
| DefineBlackboard | Specify a blackboard variable for this node's children to use. |
| SetBlackboard | Write to a blackboard variable. The variable must have already been defined. |
| ConstantResult | Always return one of the standard status codes (SUCCESS, RUNNING, or FAILURE). |
| ExecuteChoreography | Perform an uploaded choreography sequence with a specified name. |
| MissionUploadChoreography | Upload a specified group of choreography sequences and animated moves. |
| BosdynQueryStoredCaptures | Issue a QueryStoredCapturesRequest with a given QueryParameters message and write the response to a specified blackboard variable. Additional blackboard variables for action and group names can optionally be specified to be added to QueryParameters and used for the request. |
Creating a behavior tree
The following sections provide Python code that directly uses Python-compiled protocol buffers to build our behavior tree representations, also called “missions”.
All of the node types described above have a corresponding protocol buffer message definition. Each one must be wrapped by a general Node message. For example, here is a single-node mission titled “Just power on” that will power on the robot:
...
power_on = nodes_pb2.BosdynPowerRequest(service_name='power',
host='localhost',
request=power_pb2.PowerCommandRequest.REQUEST_ON)
power_on_mission = nodes_pb2.Node(name='Just power on')
power_on_mission.bosdyn_power_request.CopyFrom(power_on)
...
Simple sequence example
The following behavior tree diagram depicts a simple linear sequence of actions.
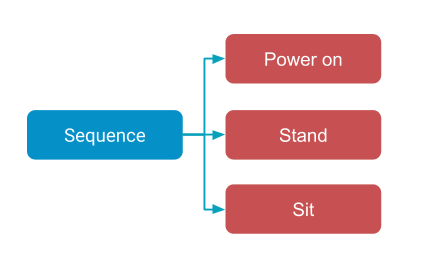
The following Python code snippet implements the simple linear behavior tree shown above using BosdynRobotCommand action nodes, plus the “Just power on” mission from before.
...
request = basic_command_pb2.StandCommand.Request()
mobility_command = mobility_command_pb2.MobilityCommand.Request(
stand_request=request)
synchronized_command = synchronized_command_pb2.SynchronizedCommand.Request(
mobility_command=mobility_command)
robot_command = robot_command_pb2.RobotCommand(
synchronized_command=synchronized_command)
stand = nodes_pb2.BosdynRobotCommand(service_name='robot-command',
host='localhost',
command=robot_command)
stand_mission = nodes_pb2.Node(name='Just stand')
stand_mission.bosdyn_robot_command.CopyFrom(stand)
request = basic_command_pb2.SitCommand.Request()
mobility_command = mobility_command_pb2.MobilityCommand.Request(
sit_request=request)
synchronized_command = synchronized_command_pb2.SynchronizedCommand.Request(
mobility_command=mobility_command)
robot_command = robot_command_pb2.RobotCommand(
synchronized_command=synchronized_command)
sit = nodes_pb2.BosdynRobotCommand(service_name='robot-command',
host='localhost',
command=robot_command)
sit_mission = nodes_pb2.Node(name='Just sit')
sit_mission.bosdyn_robot_command.CopyFrom(sit)
sequence = nodes_pb2.Sequence()
sequence.children.add().CopyFrom(power_on_mission)
sequence.children.add().CopyFrom(stand_mission)
sequence.children.add().CopyFrom(sit_mission)
mission = nodes_pb2.Node(name='Power on then stand then sit')
mission.sequence.CopyFrom(sequence)
...
More complex behavior tree example
The following behavior tree diagram shows the structure of a mission that repeats a task until either the designated number of iterations are completed or until the robot battery reaches a low-charge threshold.
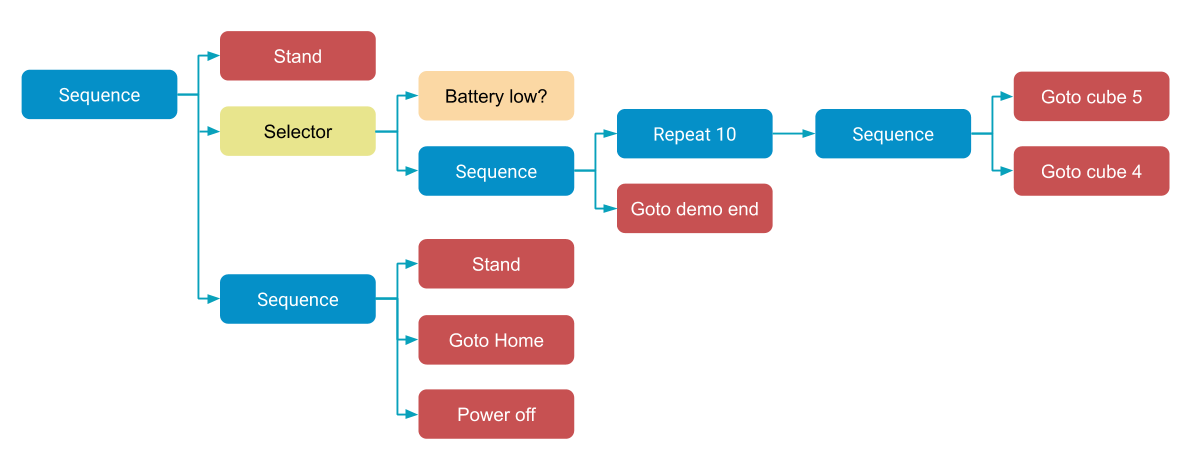
In this example, the robot stands up and then performs a demo of walking between two locations 10 times, finally going to some location labeled “demo end.” If at any point the battery is below some threshold, or the robot successfully goes to the “demo end” location, the robot will go to a location labeled “Home” and power off.
The root of the tree is a sequence that makes the robot stand, then run the selector node, then perform the “go home and power off” sequence.
The code below shows how to set up the mission, assuming the inner sequence of “Repeat 10” and “Goto demo end” is contained in the battery_high_mission and the sequence of “Stand,” “Goto Home,” and “Power off” is contained in the battery_low_mission.
First we set up the node that will query the robot state and insert it into the blackboard. Note that state_name is set to “state.” We will use that string in the Condition node.
robot_state = nodes_pb2.BosdynRobotState(service_name='robot-state',
host='localhost',
state_name='state')
Now we tell the Condition node to read power_state.locomotion_charge_percentage.value from state, and see if it is less than or equal to 20.
...
is_battery_low = nodes_pb2.Condition()
is_battery_low.lhs.var.name = 'state.power_state.locomotion_charge_percentage.value'
is_battery_low.lhs.var.type = util_pb2.VariableDeclaration.TYPE_FLOAT
is_battery_low.operation = nodes_pb2.Condition.COMPARE_LE
is_battery_low.rhs.const.float_value = 20
is_battery_low_mission = nodes_pb2.Node()
is_battery_low_mission.condition.CopyFrom(is_battery_low)
...
The Condition node must be the child of the BosdynRobotState node, in order for it to read the state out of the blackboard.
...
robot_state.child.CopyFrom(is_battery_low_mission)
robot_state_mission = nodes_pb2.Node()
robot_state_mission.bosdyn_robot_state.CopyFrom(robot_state)
...
The Selector is set to “always restart”, so that it will execute the BosdynRobotState and its Condition node child on every tick. This means that the behavior tree is reading new state from the robot and checking the battery percentage against the latest value.
...
selector_mission = nodes_pb2.Node()
selector = selector_mission.selector
selector.always_restart = True
selector.children.add().CopyFrom(robot_state_mission)
selector.children.add().CopyFrom(battery_high_mission)
sequence = nodes_pb2.Sequence()
sequence.children.add().CopyFrom(stand_mission)
sequence.children.add().CopyFrom(selector_mission)
sequence.children.add().CopyFrom(battery_low_mission)
mission = nodes_pb2.Node(name='Do A while battery % > 20, otherwise do B')
mission.sequence.CopyFrom(sequence)
...
MissionService RPCs
The MissionService provides RPCs for clients to load and play missions recorded using the GraphNavRecordingService.
| RPC | Description |
|---|---|
| LoadMission | Load a mission to run later. |
| PlayMission | Start executing a loaded or paused mission. |
| PauseMission | Pause mission execution. |
| RestartMission | Start executing a loaded mission from the beginning. |
| GetState | Get the state of the mission. |
| GetInfo | Get static information regarding the mission. |
| GetMission | Download the mission as it was uploaded to the service. |
| AnswerQuestion | Specify an answer to a question asked by the mission. |
RemoteMissionService RPCs
RemoteMissionService RPCs are called by MissionService to communicate with a robot payload. The mission service uses these RPCs to communicate with a remote mission service.
| RPC | Description |
|---|---|
| EstablishSession | Call this once at mission load time, per node. |
| Tick | Call this every time the RemoteGrpc node is ticked. |
| Stop | Call this every time the RemoteGrpc node was ticked in the previous cycle, but not ticked in this cycle. |
| TeardownSession | Tells the service it can forget any data associated with the given session. |